How Do You Calculate Forecast Error
Sometimes these two calculations are the same. It is calculated as.
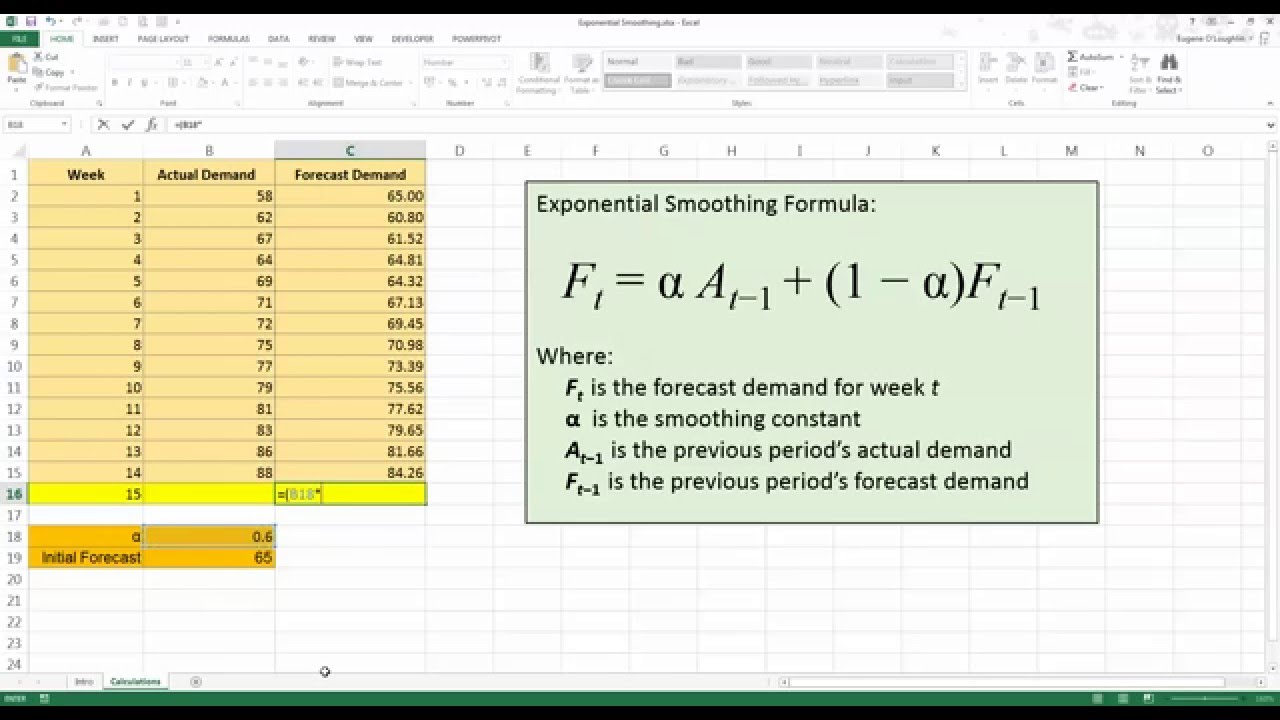
How To Forecast Using Exponential Smoothing In Excel 2013 Youtube Exponential Forecast Analysis
Essentially MAPE measures the average percentage points your forecasts are off by making it a quick and easy-to-understand way of representing forecast error.
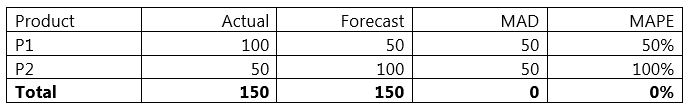
How do you calculate forecast error. MAPE 1n Σactual forecast actual 100. Some commonly used metrics include. Actual the actual data value.
We can also compare RMSE and MAE to determine whether the forecast contains large but infrequent errors. This is simply the difference between the actual volume and the forecast volume expressed as a percentage. One simple approach that many forecasters use to measure forecast accuracy is a technique called Percent Difference or Percentage Error.
Error A FA. How MAD is calculated is one of the most common questions we get. A fairly simple way to calculate forecast error is to find the Mean Absolute Percent Error MAPE of your forecast.
So this was mostly cultural. The forecast error calculation you just did is in H. MAPE mean absolute percentage error - see below.
Ive been trying to get my head around how to calculate a forecast accuracy. Here is how I usually set up a simply formula in excel. Statistically MAPE is defined as the average of percentage.
Direction The first is the magnitude of the Error The second implies bias if persistent 7 Actual Absolute Value of Actual - Forecast Error Error Absolute Value of Actual - Forecast 2007-2018 Demand Planning LLC. Mean Forecast Error MFE For n time periods where we have actual demand and forecast values. Forecast Error Forecast Error is the deviation of the Actual from the forecasted quantity Deviation vs.
If you want to examine bias as a percentage of sales then simply divide total forecast by total sales results of more than 100 mean that you are over-forecasting and results below 100 that you are under-forecasting. Identify forecast models that need adjustment management by exception Measures of Forecast Accuracy. But to do this you need to estimate how many calls youre going to receive or make on a daily and hourly basis.
Σ a fancy symbol that means sum n sample size. MSE mean squared error - the average of a number of squared errors. Making predictions about staffing needs for the year ahead is helpful for planning long-term resource needs but might not be as good for weekly rostering.
Statistically MAPE is defined as the average of percentage. MAD is calculated as follows. Calculate the error percentage by dividing F2G2.
A big part of DDMRP is its proponents stating that critics dont understand DDMRP. Forecast Error is the deviation of the Actual from the forecasted quantity. Divide by the number of data points.
First I calculate the absolute variance between sales and forecast. Since most of the demand planning evolved from Sales function MAPE was also measured this way. RMSE root mean squared error - the square root of MSE.
MAPE 1n SForecast - Actual DemandActual Demand 100. MAE mean absolute error or MAD mean absolute deviation - the average of the absolute errors across products or time periods. Forecast the forecasted data value.
For example sales of 120 over 100 will mean a 120 attainment while the error of 20 will also be expressed as a proportion of their forecast. By squaring the errors before we calculate their mean and then taking the square root of the mean we arrive at a measure of the size of the error that gives more weight to the large but infrequent errors than the mean. Error Actual demand Forecast OR et At Ft.
There are many standards and some not-so-standard formulas companies use to determine the forecast accuracy andor error. Mean Absolute Deviation MAD ABS Actual Forecast. The formula to calculate MAPE is as follows.
Σ a fancy symbol that means sum n sample size. MSE 1n Σactual forecast 2. One of the most common metrics used to measure the forecast accuracy of a model is MSE which stands for mean squared error.
One of the most common metrics used to measure the forecasting accuracy of a model is MAPE which stands for mean absolute percentage error. Ideal value 0. It is calculated as follows.
First you need to define the duration of your forecast. As shown above the traditional forecast error calculation is in E. In this article we analyze what a DDMRP proponent has.
Actual the actual data value. I do this for each individual Material product. Error absolute value of Actual Forecast A - F.
Find the mean of the actuals. Its formally referred to as Mean Percentage Error or MPE but most people know it by its formal. We take absolute values because the magnitude of the error is more important than the direction of the error.
In such a scenario SalesForecast will measure Sales attainment. MPE Actual Forecast Actual x 100. Applying this calculation to Sunday in our table above we can quickly find the error for that day is 39 percent.
I frequently see retailers use a simple calculation to measure forecast accuracy. MFE 0 model tends to under-forecast MFE 0 model tends to over-forecast. A fairly simple way to calculate forecast error is to find the Mean Absolute Percent Error MAPE of your forecast.
Add all of the errors together. Absolute variance ABSActual sales - forecast. Subtract the mean of the actuals from the forecast and use the absolute value.
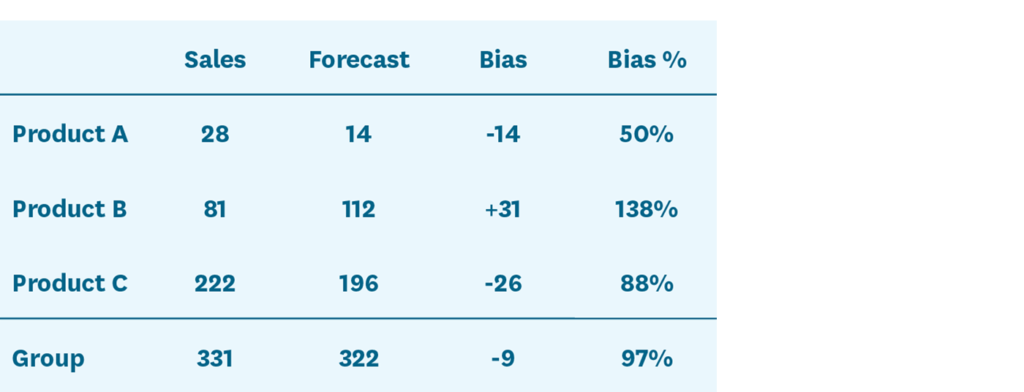
Measuring Forecast Accuracy The Complete Guide Relex Solutions

Sales Forecasting Template Templates Excel Templates Financial Budget

Data Table To Calculate Accuracy Excel Tutorials Data Table Accuracy
How To Calculate Forecast Accuracy Microsoft Power Bi Community

How To Report Forecast Accuracy To Management Supply Chain Link Blog Arkieva

Posting Komentar untuk "How Do You Calculate Forecast Error"