How To Calculate Error Statistics
The sample standard deviation divided by the square root of the number of samples. S E x s n 3486 5 3486 223 1563.
A sample population of 25 people was selected from a population of 100 people.
How to calculate error statistics. Next youll need to determine if youll use a one-tailed test or a two-tailed test. The terms standard error and standard deviation are often confused. Critical probability p 1 - Alpha 2 where Alpha is equal to 1 - the confidence level 100.
43 5 cm Percentage error The error expressed as a fraction of the value. Mean Under the Null Hypothesis. In statistics critical value is the measurement statisticians use to calculate the margin of error within a set of data and is expressed as.
Finally divide the standard deviation obtained by the square root of the number of measurements n to get the standard error of your estimate. Sample proportion P-hat n sample size z z-score. σ est Σy ŷ 2 n.
Whereas the critical area of distribution is one-sided in a one-tailed test its two-sided in a two-tailed test. 1000 people were surveyed and 380 thought that climate change was not caused by human pollution. Lets also assume that the significance level for the test is 005.
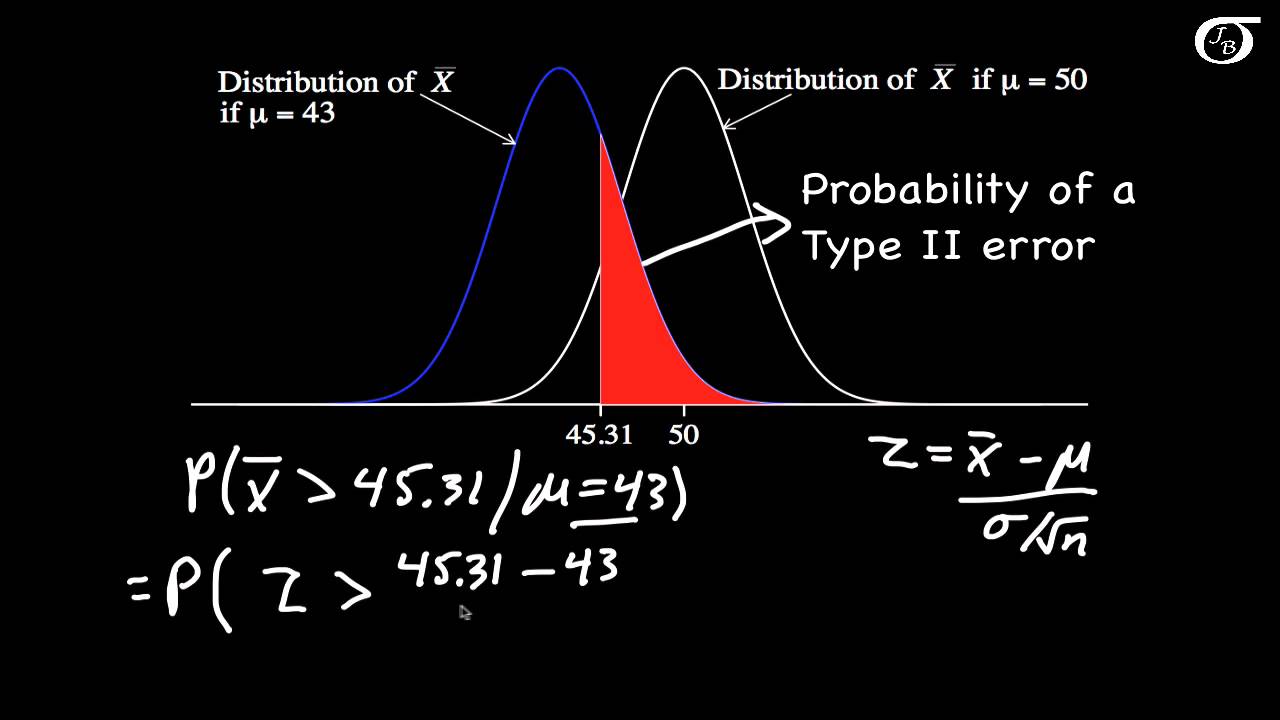
Lets assume that µ26 but we could choose any value such that the null is not correct. The probability of committing this type of error is called the beta level of a test typically denoted as β. Go through the example given below to understand the method of calculating standard error.
What we would like to now is calculate the probability of a Type II error conditional on a particular value of µ. Decide on the type of test youll use. Often denoted σ est it is calculated as.
X n x 2 1 5 1 14 54 2 36 54 2 45 54 2 70 54 2 105 54 2 1 4 1600 324 81 256 2601 3486. Take the square root of the calculated value. Multiply the result by the appropriate z- value for the confidence level desired.
The standard error of the estimate is a way to measure the accuracy of the predictions made by a regression model. Positively in this sense doesnt mean that they gave a Yes answer. Calculated automatically on most scientific calculators when you use the σ key see your calculator manual.
In statistics error refers to the difference between the value which has been computed and the correct value. The total number of observations. The standard deviation often SD is a measure of variability.
Multiply the sample proportion by 1 ρ. Absolute error The error expressed in the same dimensions as the value. To calculate the beta level for a given test simply fill in the information below and then click the Calculate button.
Calculate the standard error of the given data. Divide the result by n. This is a left tailed test 2.
The standard error of the mean is calculated using the standard deviation and the sample size. 5 10 12 15 20. Percent error experimental value - theoretical value theoretical value x 100.
This means that the larger the sample the smaller the standard error because the sample statistic will be closer to approaching the population parameter. Errors are brought about. Thus the Standard Error S E x.
Refer to the above table for the appropriate z -value. - The error on a mean can be estimated by the standard error ie. When we calculate the standard deviation of a sample we are using it as an estimate of the.
As a result we need to use a distribution that takes into account that spread of possible σsWhen the true underlying distribution is known to be Gaussian although with unknown σ then the resulting estimated distribution follows the Student t. S 1 n 1 x 1 x 2 x 2 x 2. When keeping the sign for error the calculation is the experimental or measured value minus the known or theoretical value divided by the theoretical value and multiplied by 100.
Find P-hat by dividing the number of people who responded positively. Absolute error is the magnitude of how far off a measurement is from a true value or an indication of the uncertainty in a measurement. 1 The contrast between these two terms reflects the important distinction between data description and inference one that all researchers should appreciate.
The Standard Error of the given numbers is 1563. If the confidence level is 95 percent the z -value is 196. It means that.
Sampling Error Formula refers to the formula that is used in order to calculate statistical error that occurs in the situation where person conducting the test doesnt select sample that represents the whole population under consideration and as per the formula Sampling Error is calculated by dividing the standard deviation of the population by the square root of the size of sample and then multiplying the. Therefore the standard error of the sample data is 36. In many practical applications the true value of σ is unknown.
If the estimated standard deviation of the sample population is 18 calculate the standard error of the sample population. From the formula youll see that the sample size is inversely proportional to the standard error. Find the MoE for a 90 confidence interval.
Is this always true irrespective of the.

Pin On Lean Six Sigma And Statistics

Different Symbols Of Statistics Statistics Math Statistics Symbols Ap Statistics

Sample Size Formula Calculator Sample Size Formula Data Science Learning Statistics Math

How Do I Calculate My Margin Of Error Nps Calculator Customer Experience

Posting Komentar untuk "How To Calculate Error Statistics"